Worksheet on Online Banking Application
Problem Statement:
You will create a terminal based functioning banking application using python language where:
-
You can open a Bank Account and the application will give you account number and a default password. Save the information like account number, password, bank type and then balance amount in a txt file called “accounts.txt”.
-
Implement login functionality for created accounts by reading the information from the file and checking balance.
-
Make the Account Class have properties like accountNumber, balance, accountType, savings, current, etc.
-
Implement functionality for depositing, withdrawing, and deleting personal accounts after logging in.
-
Implement sending money to other accounts and implement error handling like insufficient funds or if the receiving account exists or not.
-
Implement functionality for Types of Bank Account like BusinessAccounts & PersonalAccounts.
NOTE: Use OOP principles like Classes, Objects, Inheritance, Abstraction, etc.
Overview of the Program Structure
Classes:
-
BankAccount: The base class for creating bank accounts.
-
PersonalAccount and BusinessAccount: Subclasses that define different types of accounts.
-
BankingSystem: Manages account creation, login, transactions, and data persistence.
-
Main Function: The entry point for the application, which provides a menu-driven interface for users to interact with the banking system.
Follow the given following steps carefully:
-
Create a new python file.
-
Import the necessary packages that need to be used like the one given below, i.e random package:
-
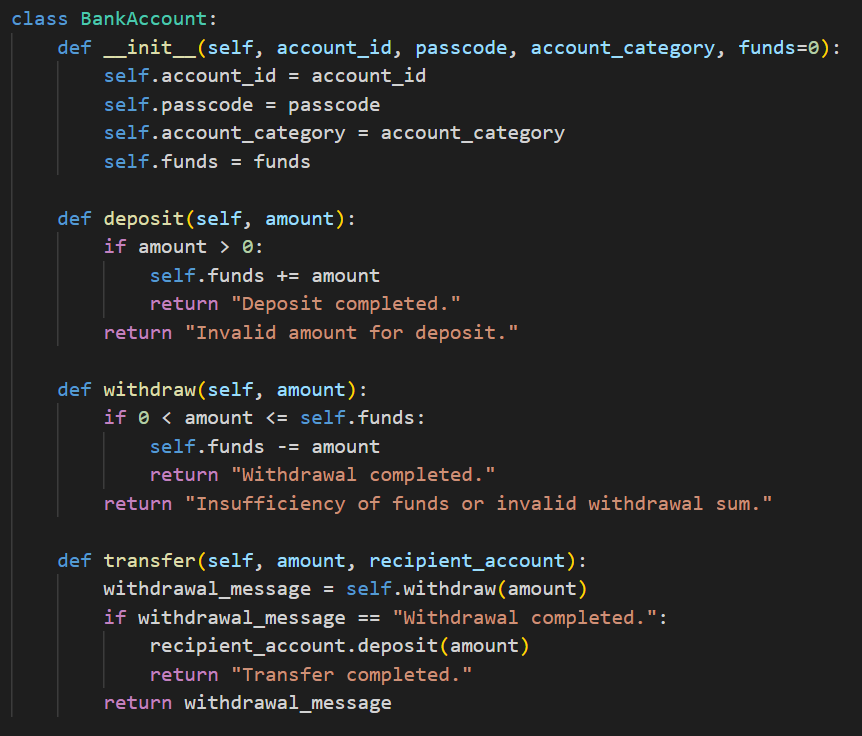
Create a BankAccount Class: The class should consist of following things: -Constructor (init): Initializes the account with an ID, passcode, category, and initial funds. Methods:
- deposit(amount): Adds funds to the account.
- withdraw(amount): Removes funds from the account if sufficient funds are available.
- transfer(amount, recipient_account): Transfers funds to another account by withdrawing from the current account and depositing it to the recipient.
-
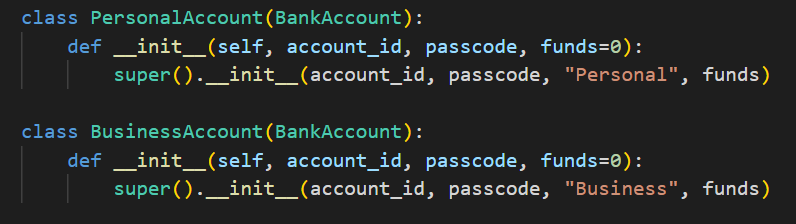
Then create a PersonalAccount and BusinessAccount Classes These classes inherit from BankAccount. They are used to create specific types of accounts (personal or business) and initialize them with the appropriate account category.
-
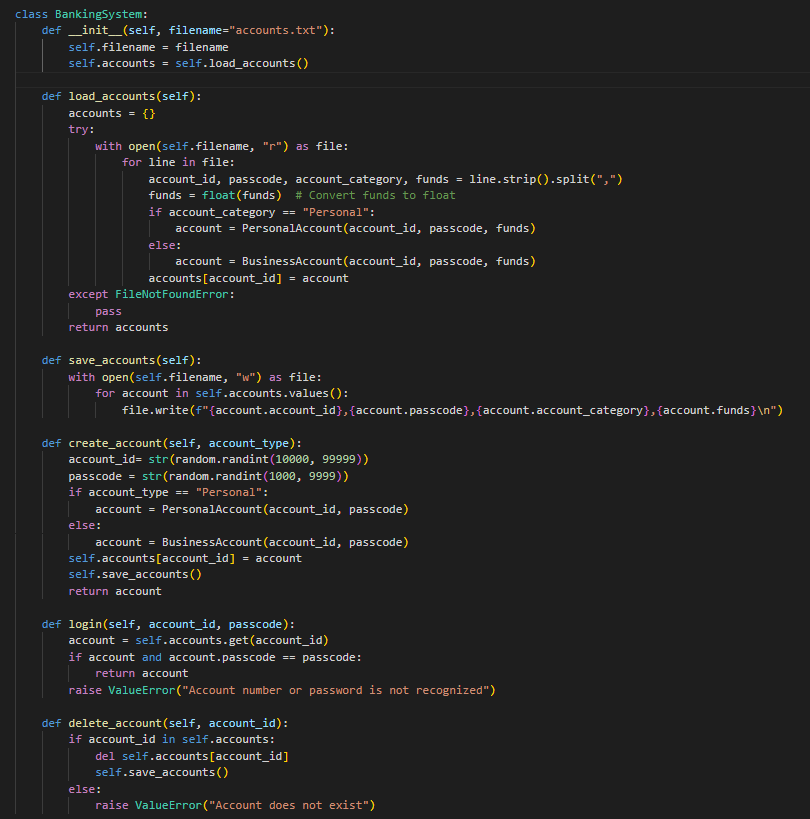
Then create a BankingSystem Class:
The BankingSystem class manages the overall banking operations, including account management, saving and loading account data, and handling user interactions. Key Methods in BankingSystem:
-
init: Initializes the system and loads existing accounts from a file.
-
load_accounts(): Reads account data from a text file and creates account instances.
-
save_accounts(): Writes the current accounts and their details back to the file.
Refer here to learn how to read/write on the file.
-
create_account(account_type): Creates a new account (personal or business) with a unique ID and passcode.
-
login(account_id, passcode): Validates login credentials and returns the corresponding account.
-
delete_account(account_id): Deletes an account from the system and updates the file.
-
-
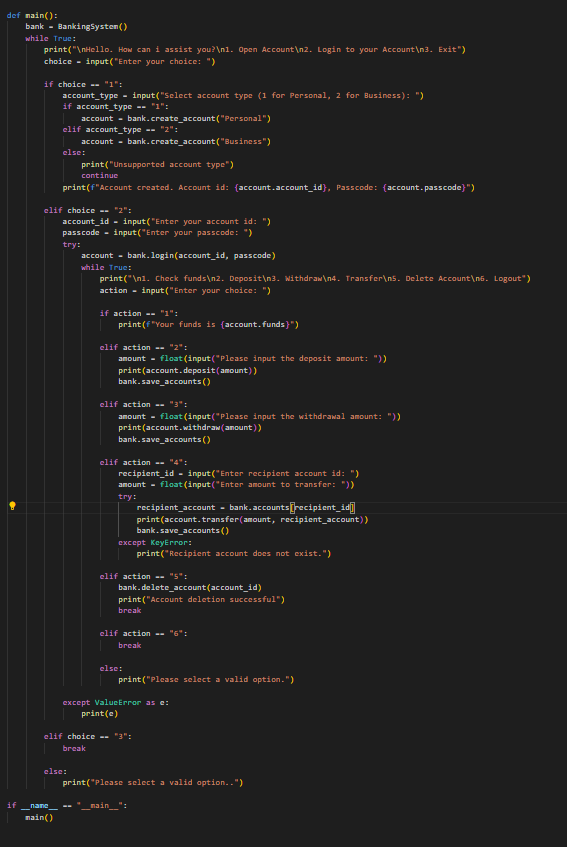
Now, create a Main Function:
The main() function provides a command-line interface for users to interact with the banking system. It displays a menu for creating accounts, logging in, and performing various banking operations.
The program starts by calling the main() function. Menu Options:
- Open Account: Users can choose to create either a personal or business account.
- Login to your Account: Users can log into their existing accounts using their account ID and passcode.
- Exit: Terminates the program.
Inside the Loop:
After logging in, users can check their balance, deposit funds, withdraw funds, transfer funds to another account, delete their account, or log out.
-
Lastly, save the python code and start executing it.
Submission Instructions:
- Comment the code based on your understanding wherever necessary.
- Push your code to the repository.
- Submit Your Work:
- Share the link to your GitHub repository in the google classroom for module tutor to review your code.