Introduction to storing data: The "WHY?"
1. Introduction to Storing Data
Why it matters:
Understanding how data is stored is fundamental to computer science and programming. It directly impacts how efficiently a program can run and how effectively it can utilize a computer's resources.
Historical context:
In the early days of computing, memory was extremely limited and expensive. Programmers had to be incredibly efficient with how they stored and manipulated data.
As computers evolved, memory became more abundant, but the principles of efficient data storage remained crucial for performance.

How computers work:
At its core, a computer stores data in binary format (0s and 1s) in its memory. How this data is organized and accessed can significantly affect the speed and efficiency of operations.
Different data structures provide different ways to organize this binary data for various use cases.
Evolution:
As programming languages evolved from low-level (like assembly) to high-level languages, abstractions were created to make data storage more intuitive. However, understanding the underlying principles remains crucial for writing efficient code.
2. Static vs Dynamic Data Structures
Why it matters:
The choice between static and dynamic data structures impacts memory usage, performance, and the flexibility of your program. Understanding both types allows programmers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs.
How computers work:
- Static structures: These have a fixed size, allocated at compile time. They're stored in a part of memory called the stack, which is fast but limited in size.
- Dynamic structures: These can grow or shrink at runtime. They're stored in the heap, a larger but slower part of memory.
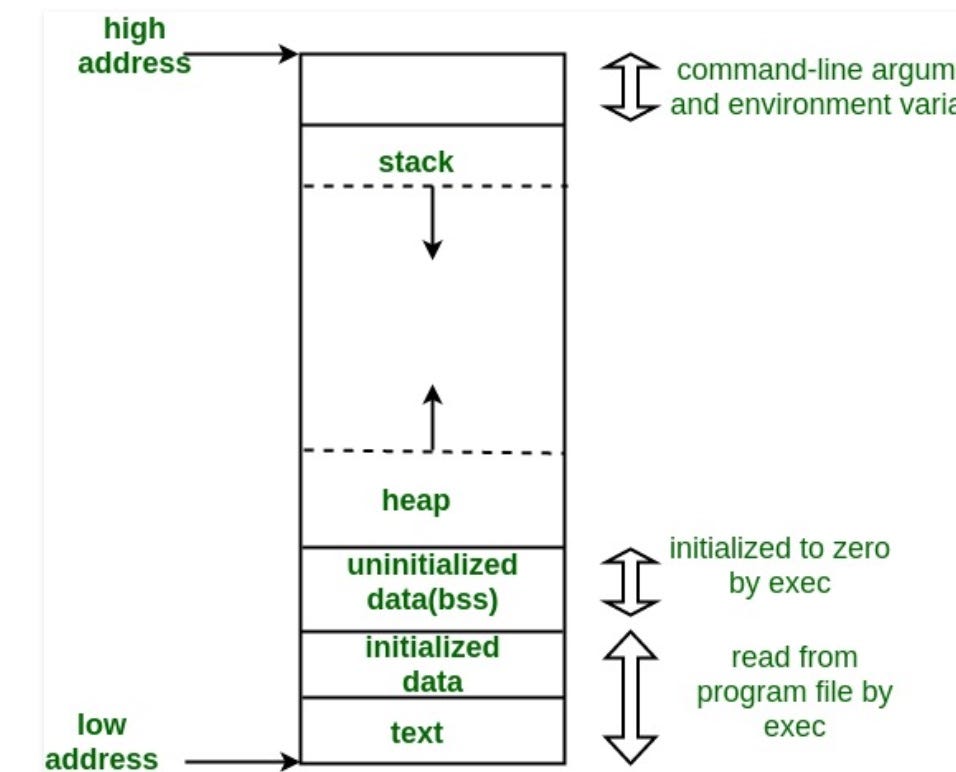
Historical context:
Early programs primarily used static structures due to limited memory and the need for predictability. As memory became more abundant and programs more complex, dynamic structures became increasingly important.
Evolution:
- Early days: Programs used mostly static arrays and structures.
- Introduction of pointers: Allowed for more flexible memory management.
- Development of dynamic allocation: Enabled the creation of data structures that could grow and shrink as needed.
- Modern era: High-level languages often abstract away the details, but understanding the underlying principles remains crucial for optimization.
Impact on programming:
- Static structures are still used for their speed and simplicity in certain scenarios.
- Dynamic structures enable more flexible and scalable programs, crucial for modern software development.
- Understanding both allows programmers to make informed decisions based on performance needs, memory constraints, and problem requirements.
In conclusion, learning about data structures, including the fundamental concepts of data storage and the distinction between static and dynamic structures, is essential for any programmer. It provides the foundation for writing efficient, scalable, and robust software, regardless of the evolution of computer hardware and programming languages.